By ESG Analyst Tilley Woodford
What is satellite monitoring?
In recent years satellite monitoring technology has been utilized to identify where greenhouse gases are being released and to map where emissions are most concentrated. Satellites can be natural or artificial objects that are orbiting around the earth, other planets, or stars. Man-made satellites are commonly sent into orbit to collect information for various scientific purposes (Canadian Space Agency, 2022). These satellites can capture images of the Earth’s surface and determine information about the greenhouse gas emissions in that area, specifically the concentrations of methane and carbon dioxide that are present. This data is very useful because it helps scientists determine where the most greenhouse gases are being released and what is producing them. Furthermore, more up-to-date information is available through satellite monitoring compared to traditional methods of greenhouse gas measurements. These satellites can also monitor the prevalence of fires by detecting the surface temperatures and can survey the changes in land use, for instance, the occurrence of deforestation and forest deterioration. In addition, satellite observations provide a unique opportunity to enhance the global estimates of greenhouse gas emissions and to advance researchers’ understanding of changes happening to the earth and its atmosphere due to human activities (Hardwick & Grave, 2016).
How does this help the climate crisis?
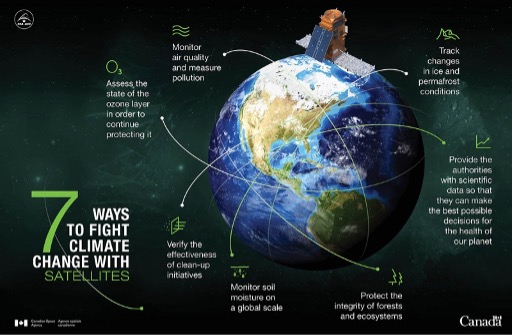
In the past, efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have relied on data and information that is self-reported by member countries of the United Nations (UN). However, this approach has encountered several issues, including missing, inaccurate, and outdated data. So, methods such as satellite monitoring offer a more efficient and accurate means of collecting emissions data. For example, the organization Climate TRACE discovered that in 2022 the emissions data collected by the UN only accounted for half of the actual emissions that were released. This discrepancy underscores how inaccurate self-reporting is and highlights the usefulness of satellite technology in obtaining an accurate understanding of the climate crisis. By collecting accurate data, scientists and researchers can make informed decisions and implement initiatives to combat global warming based on a representative understanding of the situation, rather than relying on misleading data (Edmond, 2023). In summary, some of the main ways satellites are used to fight climate change are by observing changes in permafrost conditions, measuring pollution and air quality, tracking changes in the ozone layer, analyzing the impacts of mitigation initiatives, examining soil moisture, and supplying accurate data (Canadian Space Agency, 2022).
What’s next?
The data collected by satellites helps scientists plan and alter their strategies based on the efficacy of their initiatives. The climate crisis is constantly changing and developing so this up-to-date data is critical in allowing leaders and policy makers to adjust their programs in accordance with climate trends. One of the most important aspects of mitigating climate change is being aware of current issues and having the tools to anticipate future changes, a role which satellite monitoring facilitates (Canadian Space Agency, 2022). Therefore, this data can be used to help mitigate the impacts of natural disasters that are a result of climate change. Natural disasters like hurricanes and floods can be detrimental to the functioning of entire cities, so by utilizing satellite data, authorities can be better prepared in the case of emergencies. Furthermore, Canada and the other countries involved in the Paris Climate Change Conference (COP21) were able to utilize the data collected by Canadian satellites to guide their deliberations (Government of Canada, 2022). Overall, technological advancements such as satellite monitoring and other space instruments have played a vital role in monitoring climate change and expanding our capacity to mitigate its impacts. Looking to the future, like satellite monitoring, there are many new innovations and tools that can be used to combat carbon emissions. For instance, renewable energy technologies, carbon capturing, electric vehicles, and sustainable agriculture (Acton et al., n.d.).
References
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2023/02/climate-emissions-satellite-tracking/ (Edmond, 2023)
https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/grantham-institute/public/publications/briefing-papers/Satellite-observations-to-support-monitoring-of-greenhouse-gas-emissions-Grantham-BP-16.pdf Hardwick, Stephen, and Heather Graven. “Satellite observations to support monitoring of greenhouse gas emissions.” Grantham Institute Briefing paper 16 (2016).
https://www.sap.com/canada/insights/viewpoints/by-land-sea-and-air-emerging-technologies-to-tackle-climate-change.html (Acton et al., n.d.)
https://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/satellites/everyday-lives/climate-change.asp (Government of Canada, 2022)
